In the dynamic landscape of entrepreneurship, businesses often fall into two distinct categories: those racing towards rapid expansion, attracting professional investors seeking high returns, and those opting for moderate growth with a keen focus on nurturing quality relationships, customers, and stakeholders. Understanding the differences between these two approaches is crucial for entrepreneurs as they shape their business strategies, revenue models, and funding avenues.
High-Growth, Fast-Scale Businesses
1. Aggressive Expansion Strategies:
High-growth ventures prioritize rapid expansion into new markets, both domestic and international. Their primary goal is to capture market share quickly and establish a dominant position in their industry.
2. Professional Investor Attraction:
These businesses often seek funding from professional investors such as venture capitalists, private equity firms, and angel investors. The influx of capital enables them to invest heavily in marketing, research and development, and scaling operations.
3. Focus on Scalability:
High-growth businesses prioritize scalability in their operations. Their products or services are designed to reach a broad audience, leveraging economies of scale to drive down costs and increase profitability.
4. Risk-Taking Culture:
Given the aggressive growth targets, these businesses are generally more comfortable taking calculated risks. Innovation and disruption are key components of their DNA, as they constantly seek to outpace competitors and stay ahead of market trends.
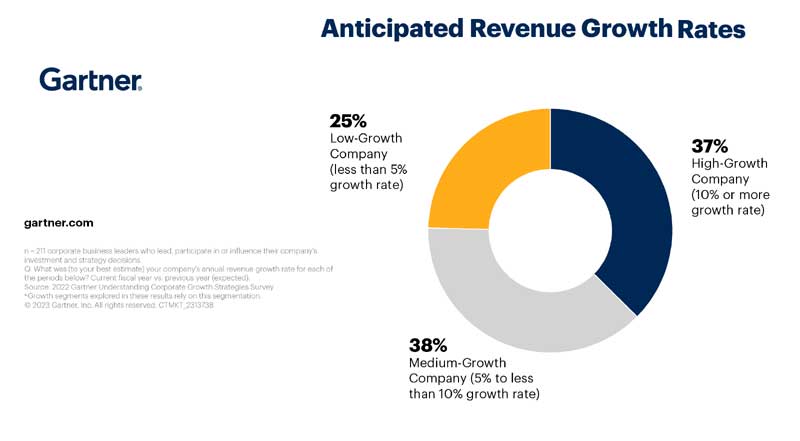 Anticipated revenue growth rates. (Gartner)
Anticipated revenue growth rates. (Gartner)
Moderate Growth, Customer-Focused Businesses
1. Community-Centric Approach:
Businesses with a local focus prioritize building strong relationships within their community. They often tailor their products or services to meet the specific needs of their local customer base.
2. Customer-Centric Operations:
Customer satisfaction and loyalty are paramount for moderate growth businesses. They invest in personalized customer experiences, feedback mechanisms, and local marketing strategies to strengthen ties with their customer base.
3. Self-Funding or Small Business Loans:
Instead of relying on external investors, these businesses may opt for self-funding or seek small business loans. This approach allows them to maintain greater control over their operations and decision-making processes.
4. Sustainable Growth Practices:
Sustainability and responsible business practices are integral to the philosophy of moderate growth businesses. They prioritize long-term stability and are often deeply embedded in the social and environmental fabric of their local communities.
Revenue Approaches
High-Growth Businesses:
- Typically focus on rapid revenue growth, often at the expense of short-term profitability.
- May prioritize customer acquisition over immediate profitability, with the expectation that economies of scale will lead to profitability in the future.
Moderate Growth Businesses:
- Emphasize sustainable revenue growth with a focus on profitability from the outset.
- May prioritize customer retention and repeat business over aggressive customer acquisition strategies.
Funding Approaches:
High-Growth Businesses:
- Rely on professional investors for large capital injections.
- Common funding rounds include seed funding, Series A, B, and so on.
Moderate Growth Businesses:
- Tend to be more self-reliant or seek smaller funding options.
- May rely on small business loans, personal savings, or profits generated from operations.
Choosing the right path - fast or slow?
So it comes down to this.
Founders at the crossroads of deciding between fast scaling and a slower, more considered approach to growth must carefully weigh several crucial considerations.
Ultimately, the decision hinges on a delicate balance between seizing immediate opportunities and ensuring the business's enduring success in the long run.
Rapid scaling often demands significant financial investment and embraces a higher level of risk, catering to those who thrive in dynamic, competitive environments. Conversely, a measured growth strategy allows founders to focus on building strong foundations, understanding their market thoroughly, and fostering quality relationships.
Founders should reflect on their risk tolerance, long-term vision, and industry dynamics. Assess the market landscape, recognizing whether speed or sustainability aligns better with the business model. Prioritize understanding customer needs, as a slower approach might offer a deeper understanding of market nuances.
In truth, financial means might dictate that slow and steady is the default approach as cash becomes the limiting factor. Ultimately, the decision hinges on a delicate balance between seizing immediate opportunities and ensuring the business's enduring success in the long run.
Conclusion:
Both high-growth, fast-scale businesses and moderate growth, local-focused businesses have their unique strengths and challenges. The choice between the two approaches depends on the entrepreneur's goals, industry dynamics, and the values they prioritize. While high-growth ventures chase the allure of rapid success and scalability, moderate growth businesses seek to build lasting connections within their local communities, demonstrating that success in entrepreneurship comes in various shapes and sizes.